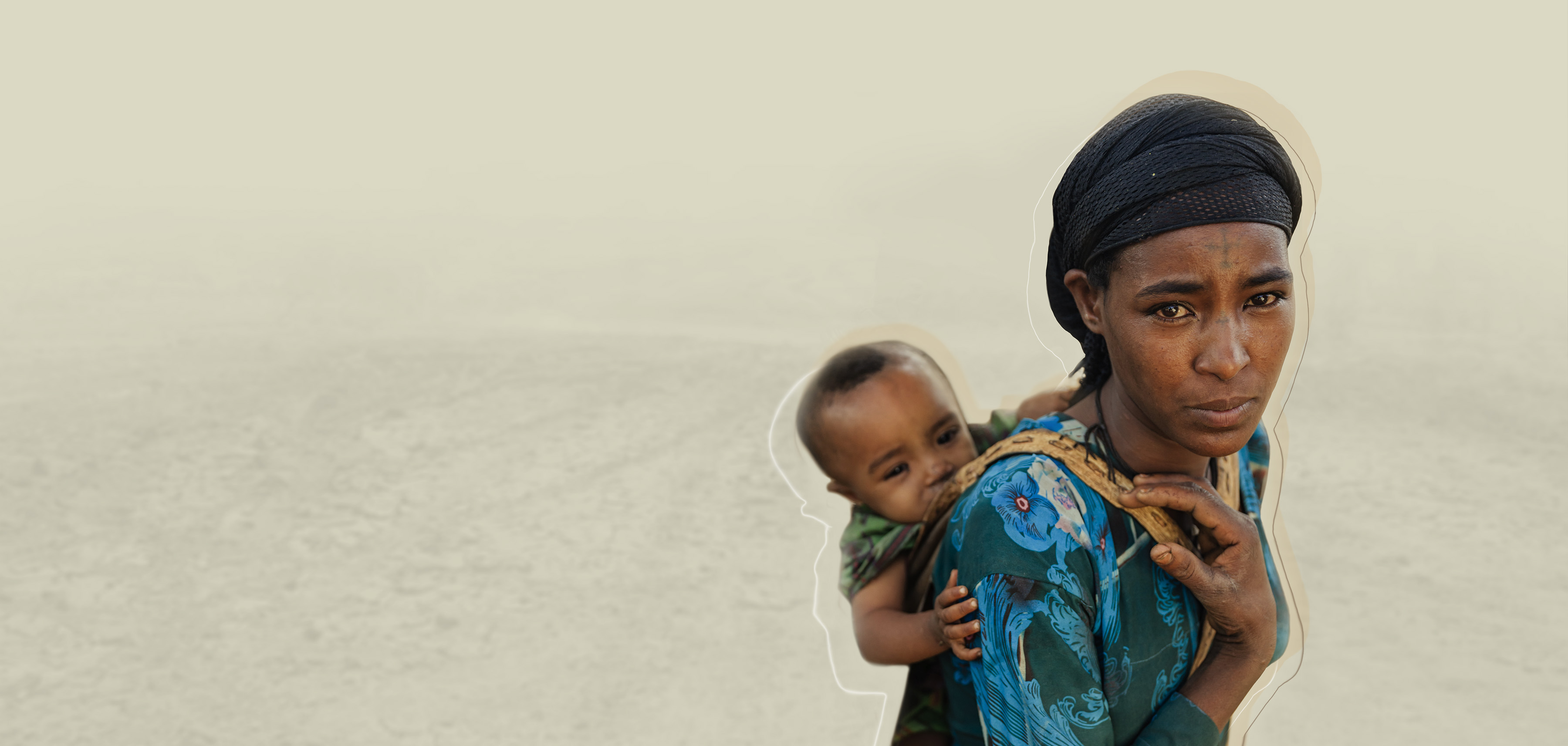
What is Maternal Mortality?
Maternal mortality is the death of a woman during childbirth or within the six weeks following the end of the pregnancy due to complications relating to or exacerbated by the pregnancy or its management.
The Causes
Pre-existing conditions such as malaria, HIV/AIDS, and cardiovascular disease may be aggravated during pregnancy. Listed below are major complications that account for 75% of all maternal deaths.
Severe bleeding and infections

High blood pressure (pre-eclampsia and eclampsia)

Unsafe abortions
Delivery complications
Complications both during and after pregnancy and labor are often preventable and treatable.
The Victims
Approximately 99% of maternal deaths occur in developing countries, primarily in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
The Treatments
Technological advancements have allowed healthcare workers to effectively combat these issues — common preventative measures are available.

Access to Antenatal Care
Proper Care and Support During and After Childbirth

Medications to Prevent Convulsions and Excessive Bleeding
The Solution
It is vital for us to take drastic measures to improve maternal health around the world. This may include:
Give adolescent girls access to high-quality pregnancy & reproductive education as well as STI prevention
Create to reliable information, counseling, and quality services
Set a global standard for maternal and newborn care
Keep health care workers accountable for the quality of care provided
Address the inequalities faced by women in poorer countries, regardless of income or location
Implement more affordable, accessible, and effective treatments and health systems